ISRO Successfully Manages Safe Re-entry of POEM-4 Module
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) marked another milestone in responsible space operations with the successful re-entry of its POEM-4 module. This event, which took place on April 4, 2025, underscores ISRO’s continued efforts in promoting space sustainability and reducing orbital debris.
POEM-4 Deployed After PSLV-C60 Launch
On 30 December 2024, ISRO launched the PSLV-C60 mission, which carried twin SPADEX satellites into space. After placing the satellites into a 475 km orbit, the mission’s upper stage—referred to as the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module or POEM-4—remained in a similar orbit.
ISRO then performed engine restarts to lower POEM-4 into a circular orbit of 350 km with an inclination of 55.2 degrees. After completing its mission, the upper stage was passivated. This involved venting leftover fuel, an important safety measure to reduce any chance of explosion or collision.
24 Payloads Operated Successfully in Orbit
During its operational life, POEM-4 hosted 24 payloads in total. Fourteen of these were developed by ISRO, while the remaining ten came from various non-governmental entities (NGEs). All payloads functioned as expected, delivering useful scientific data. This success further showcased ISRO’s capability to integrate and manage diverse payloads in a single orbital platform.
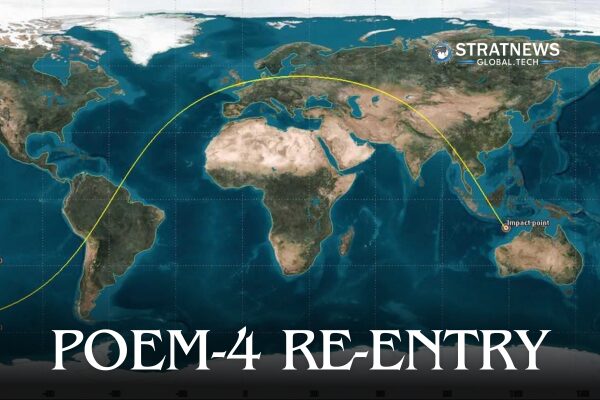
Monitored Re-entry Reaffirms ISRO’s Space Debris Goals
ISRO, in coordination with US Space Command (USSPACECOM), tracked POEM-4’s orbit during its time in space. As its orbit gradually decayed to 174 km by 165 km, predictions indicated an imminent atmospheric re-entry.
ISRO’s System for Safe and Sustainable Space Operations Management (IS4OM) closely monitored the situation. It provided regular updates to ensure accurate forecasting. At 02:33 UTC (08:03 IST) on April 4, 2025, POEM-4 safely re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and fell into the Indian Ocean.
This planned and monitored re-entry reflects ISRO’s commitment to limiting the build-up of space debris. It supports the organisation’s broader Debris Free Space Mission (DFSM) and reinforces India’s role in sustainable space operations.